Knowledge as Movement and Dwelling
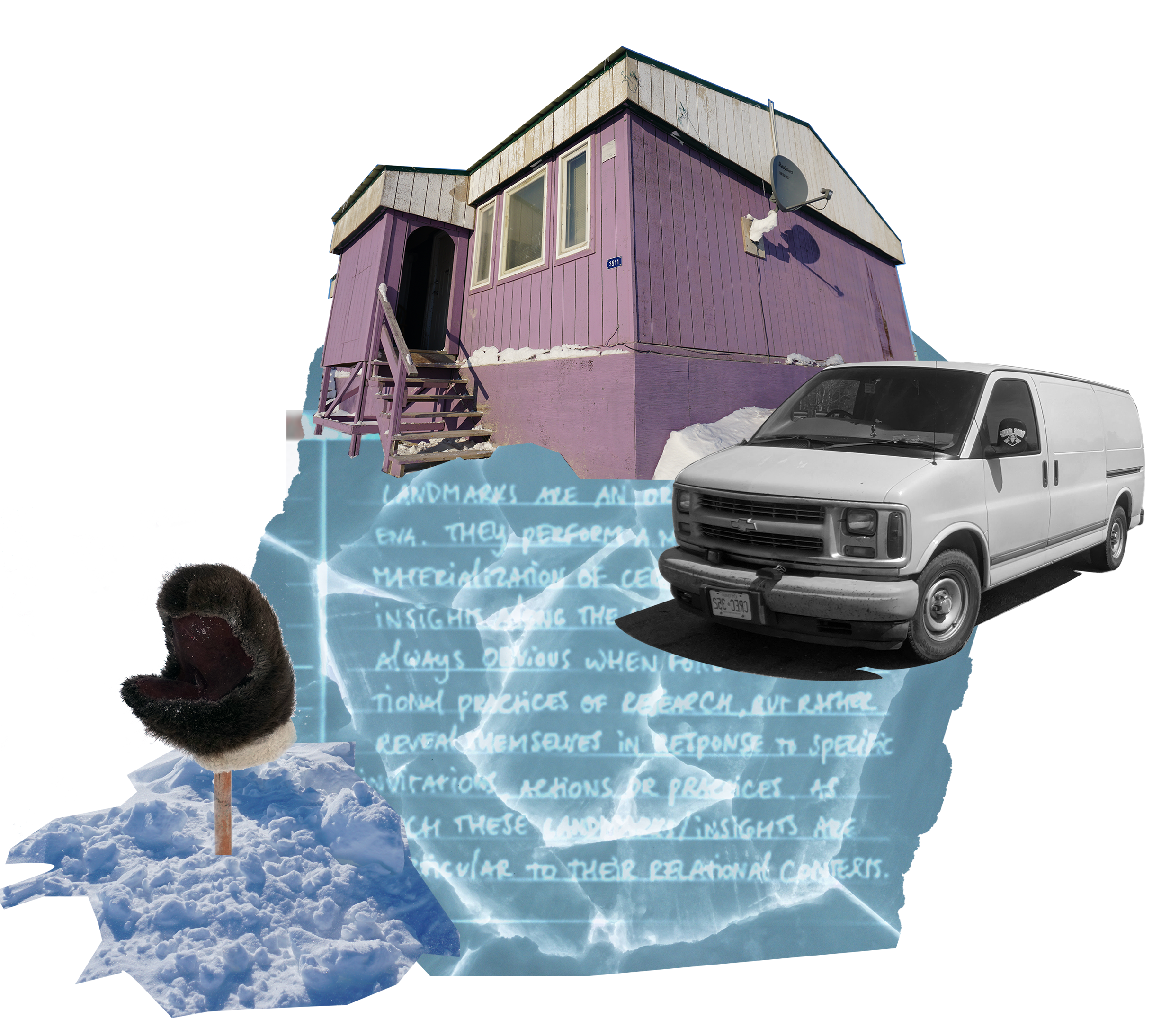
Landmarks are defining features in the land that traditionally play an important role in Inuit topographical understandings of their land and its resources. They are important orienting features to keep one's bearing while travelling and to determine where one is located at any given moment[1].
As a figure in this Knowledge-Land-Scape, "Landmarks" perform the materialization of certain findings and emergent insights along the way.
This particular one, marks my understanding of how some knowledge only comes into being through movement- or may only exist as movement.
"Becoming nomadic" , the notion of transience and of "passing", as Rosi Braidotti refers to such ways of knowing, binds us to multiple others in a web of complex interrelations, kinship, social bonding and flexible citizenship [2]. This is not knowledge that can be learnt from a book, nor is it knowledge that can be categorized or transferred for shared understanding outside of its relational events[3]. As Ingold points out elsewhere, this kind of knowledge references the world, not other books[4]
My continous moving in-between countries, territories, timezones, languages, cultures, relationships allowed for intra-relational thinking across entities and events, rather than inter-relational thinking merely between entities and events. It started to create tentative opening in which my campervan Butter, the covid-virus, hot tarmac, the seasons, vaccines, all became agents in the production of space, time, meaning and matter within my research, instead of the other way around. Slowly, I started to understand that any knowledge generated outside of the Cartesian cut, requires attunement to the agential forces of its relational web as you move through and alongside all the entities and events that are part of them. When the knowledge you seeks comes from such a relational paradigm, it are also all those relations that set the pace.
"Return" to Cut 1: Voices of Thunder, if you were seeking to collaborate with the Gjoa Haven HTA - but you got redirected by the Covid-19 pandemic.
Or,
- ↑ Aporta, C. (2004). Routes, trails and tracks: Trail breaking among the Inuit of Igloolik. Études/Inuit/Studies, 28(2), 9-38.
- ↑ Braidotti, R. (2006 p.271). Transpositions: On nomadic ethics. Polity.
- ↑ Ingold, T. (2022). On not knowing and paying attention: How to walk in a possible world. Irish Journal of Sociology, 31(1), 20-36.
- ↑ Ingold, T. (2013 p.15). Making: Anthropology, archaeology, art and architecture.
- ↑ Council, I. C. (2022). Circumpolar Inuit Protocols for Equitable and Ethical Engagement.